Overview of Inheritance
Inheritance is the capability of one class to acquire properties and characteristics from another class. The class whose properties are inherited by other class is called the Parent or Base or Super class. And, the class which inherits properties of other class is called Child or Derived or Sub class.
Inheritance makes the code reusable. When we inherit an existing class, all its methods and fields become available in the new class, hence code is reused.
NOTE : All members of a class except Private, are inherited
Purpose of Inheritance
- Code Reusability
- Method Overriding (Hence, Runtime Polymorphism.)
- Use of Virtual Keyword
Basic Syntax of Inheritance
class Subclass_name : access_mode Superclass_name
While defining a subclass like this, the super class must be already defined or atleast declared before the subclass declaration.
Access Mode is used to specify, the mode in which the properties of superclass will be inherited into subclass, public, privtate or protected.
Example of Inheritance
class Animal
{ public:
int legs = 4;
};
class Dog : public Animal
{ public:
int tail = 1;
};
int main()
{
Dog d;
cout << d.legs;
cout << d.tail;
}
Output :
4 1
Inheritance Visibility Mode
Depending on Access modifier used while inheritance, the availability of class members of Super class in the sub class changes. It can either be private, protected or public.
1) Public Inheritance
This is the most used inheritance mode. In this the protected member of super class becomes protected members of sub class and public becomes public.
class Subclass : public Superclass
2) Private Inheritance
In private mode, the protected and public members of super class become private members of derived class.
class Subclass : Superclass // By default its private inheritance
3) Protected Inheritance
In protected mode, the public and protected members of Super class becomes protected members of Sub class.
class subclass : protected Superclass
Table showing all the Visibility Modes
| Derived Class | Derived Class | Derived Class | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base class | Public Mode | Private Mode | Protected Mode |
| Private | Not Inherited | Not Inherited | Not Inherited |
| Protected | Protected | Private | Protected |
| Public | Public | Private | Protected |
Types of Inheritance
In C++, we have 5 different types of Inheritance. Namely,
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance (also known as Virtual Inheritance)
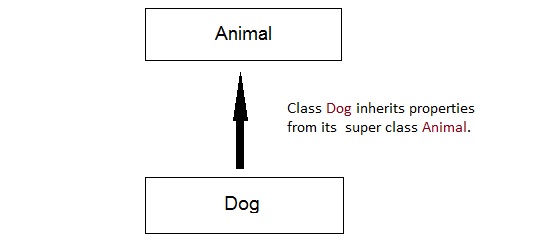
Single Inheritance
In this type of inheritance one derived class inherits from only one base class. It is the most simplest form of Inheritance.
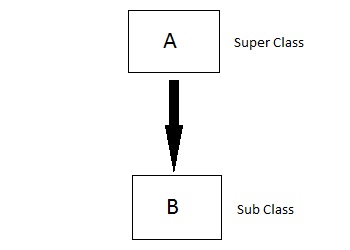
Multiple Inheritance
In this type of inheritance a single derived class may inherit from two or more than two base classes.
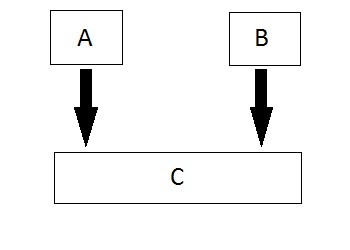
Hierarchical Inheritance
In this type of inheritance, multiple derived classes inherits from a single base class.
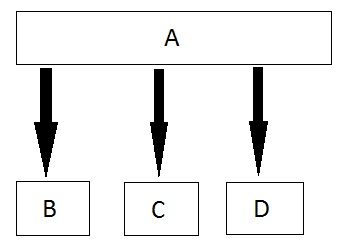
Multilevel Inheritance
In this type of inheritance the derived class inherits from a class, which in turn inherits from some other class. The Super class for one, is sub class for the other.
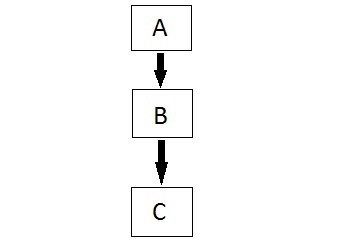
Hybrid (Virtual) Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance is combination of Hierarchical and Mutilevel Inheritance.

No comments:
Post a Comment